25 high protein breakfast ideas
Whether you eat breakfast at the crack of dawn or when the sun is high in the sky, if you make it a high protein meal, you’ll set yourself up for the rest of the day.By eating more protein, you’ll be more apt to lose weight and body fat while retaining muscle and keeping your metabolism high.1
This practical guide gives you lots of tips and ideas for delicious high protein breakfasts that include much more than ham and eggs.
At the end of this guide, we’ll briefly explain the scientific evidence about why you should prioritize protein at the start of your day, and we’ll link to key research.




Key takeaways
Why protein for breakfast?Eating high-protein foods first thing reduces hunger all day, helping you to you lose weight — and improve your body composition and metabolic health.
Eggs are a great option:
Eggs are a versatile protein source, with so many ways to prepare them, including fast grab-and-go options as well as ways that disguise their eggy nature.
Try other high-protein foods
Not a fan of eggs? Try high-protein yogurt, cheese, fish, meat, tofu, smoothies, or even leftovers. These can also be the basis of filling and nutritious high-protein breakfasts.
High protein defined
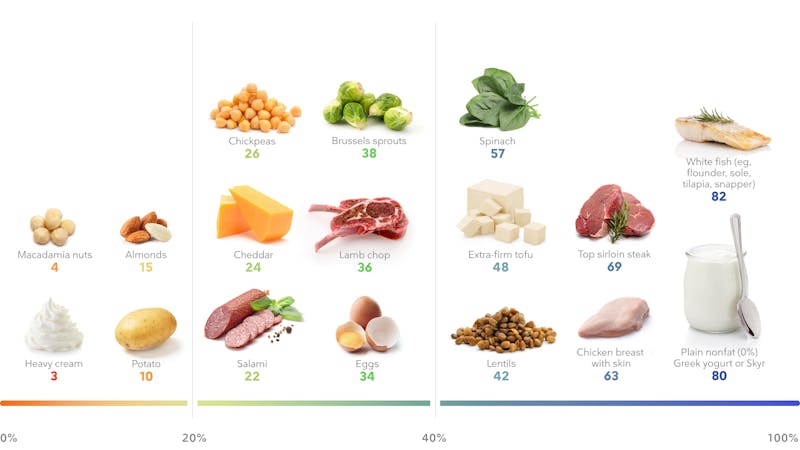
Diet Doctor defines a high-protein breakfast as one that provides at least 25 grams of protein per serving and has a protein percentage of 25% or higher.The protein percentage tells you how much of a food’s calories come from protein as opposed to fat and net carbs.2 The higher the percentage, the more protein-dense the breakfast (and the more protein and satiety per calorie, too).
Depending on your height and your goals for reducing body fat, you may want to eat 30 to 40 grams of protein at each meal if you are an average-sized woman and 35 to 50 grams if you are an average-sized man.
Refer to this chart to find your suggested daily minimum protein target based on your height.
Minimum daily protein target
| Height | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| Under 5’4″ ( < 163 cm) | 90 grams | 105 grams |
| 5’4″ to 5’7″ (163 to 170 cm) | 100 grams | 110 grams |
| 5’8″ to 5’10” (171 to 178 cm) | 110 grams | 120 grams |
| 5’11” to 6’2″ (179 to 188 cm) | 120 grams | 130 grams |
| Over 6’2″ (188 cm+) | 130 grams | 140 grams |
If you are just starting out eating a higher protein diet, you can increase your protein grams and percentage slowly to see how you feel and how your body responds.
In each of the recipes in this guide, we provide the protein amount in grams per serving and the protein percentage per serving.
We have included a few options that are just below a protein percentage of 25% for variety and to allow more choice for those who want to increase protein slowly.
Whatever the recipe, if you want to add more protein, include an extra egg white, or serve a side dish of another high protein food. Try adding sliced ham, bacon, cheese, yogurt, cottage cheese, smoked salmon, or another protein source like dairy, meat, fish, or legumes. Serve any of those on a bed of veggies or greens.
Instead of just coffee, tea, or water, if you want a higher protein drink to go with your breakfast, try our dairy-free keto latte, which blends a whole egg and coconut oil into your morning cup of coffee. That’s an extra 6 grams of protein.
On a final note, many people like to do time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting, eating only two meals a day, often just lunch and dinner. If that is your preferred pattern, aim to get even more protein in your first meal of the day — at whatever time you eat it — so that you meet your daily protein targets over your two meals.
Let’s get started.

– Access the Diet Doctor Eat premium app
– Weight loss programs to reach your goals
Egg recipes








A large egg has about 6 grams of protein. To reach a high protein target, women should eat at least three eggs and men should eat four eggs at a sitting, along with another source of protein.
But it’s your choice how you cook them: boiled, poached, fried, scrambled, baked, or cracked into a new recipe.
Did you know that Diet Doctor has more than 80 egg recipes? You’re sure to find ones you like if you scroll through the many possibilities.
Here are nine delicious high protein egg recipes to whet your breakfast appetite:
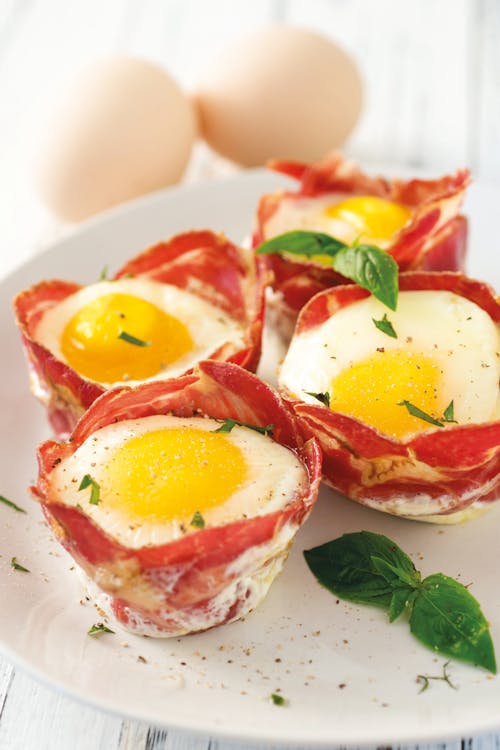
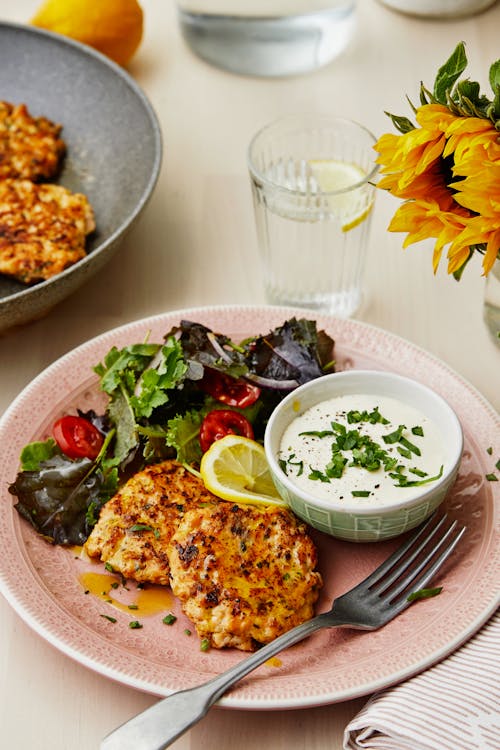
- High-protein breakfast with eggs, ham, and spinach
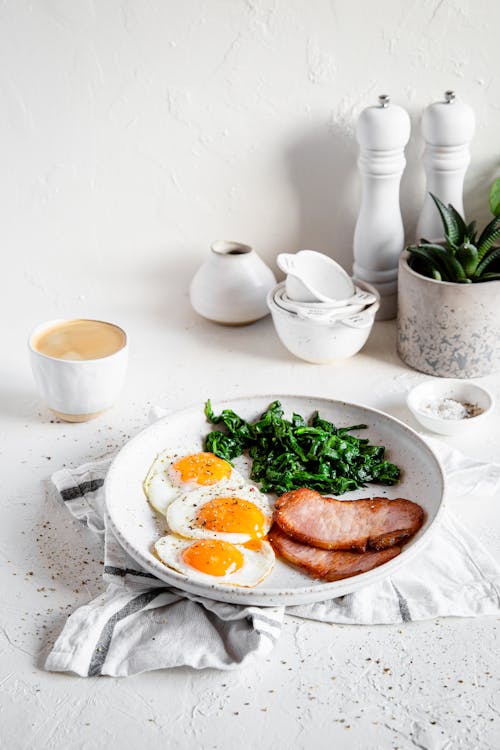
What could be simpler? Three fried eggs (or four if you’re a guy) sunny-side up, or any way you like them. They’re served with a couple of slices of fried Canadian bacon (also called back bacon, or rashers in the UK). The side of steamed spinach adds lots of fiber and nutrients. Protein: 31 grams; Protein percentage: 33% - Jill’s cheese-crusted omelet
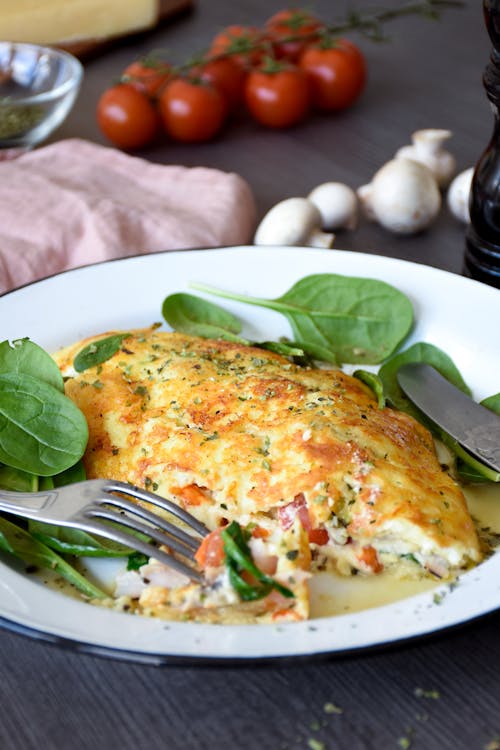
A perennial Diet Doctor favorite, this omelet’s crispy outer crust made of cheese takes this recipe to the next level. Protein: 39 grams; Protein percentage: 26% - Keto Caprese omelet
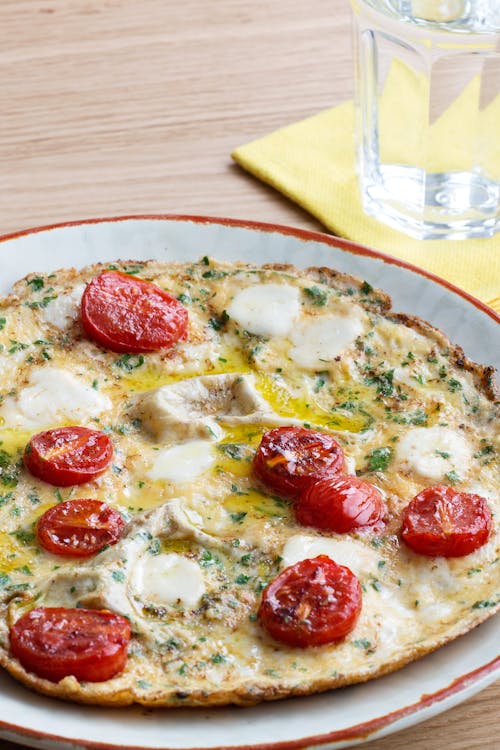
Another omelet? Ah, but this vegetarian one is so different! Showcasing eggs’ versatility, this recipe combines soft mozzarella, fresh basil, and tomatoes in a pizza-style, open-face presentation. A completely different omelet experience. Protein: 33 grams; Protein percentage 25%. - Everything-but-the-bagel omelet
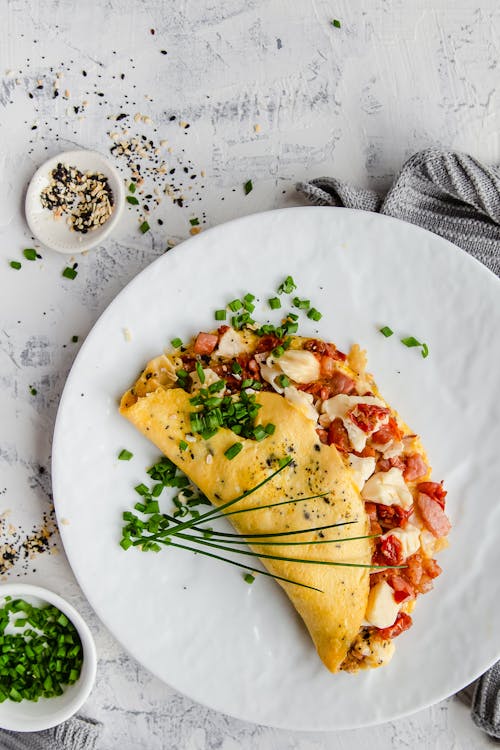
What? Another omelet? But with such a different flavor with its deli turkey, bacon, cream cheese and sun-dried tomatoes. Protein 35 grams: Protein percentage 30%. - Capicola egg cups
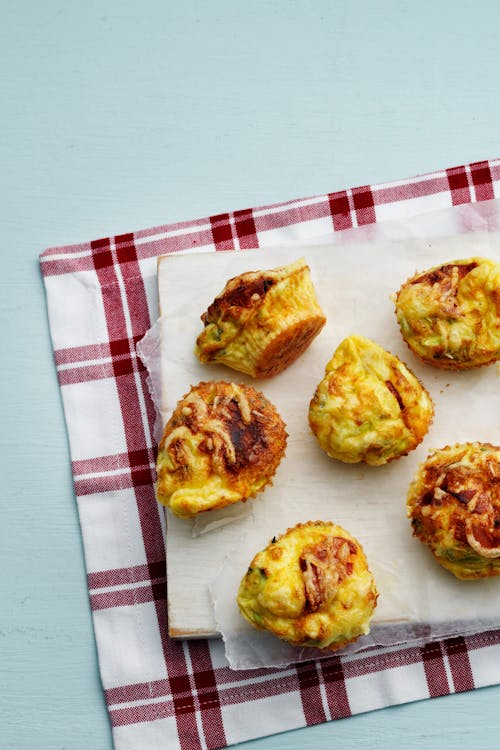
Thin slices of capicola ham line a muffin tin and create the ideal crispy cup to hold these cheesy baked eggs. Make them Sunday to have a fast breakfast option to reheat during the week. Protein (for three egg cups): 36 grams; Protein percentage: 32% - Keto egg muffins
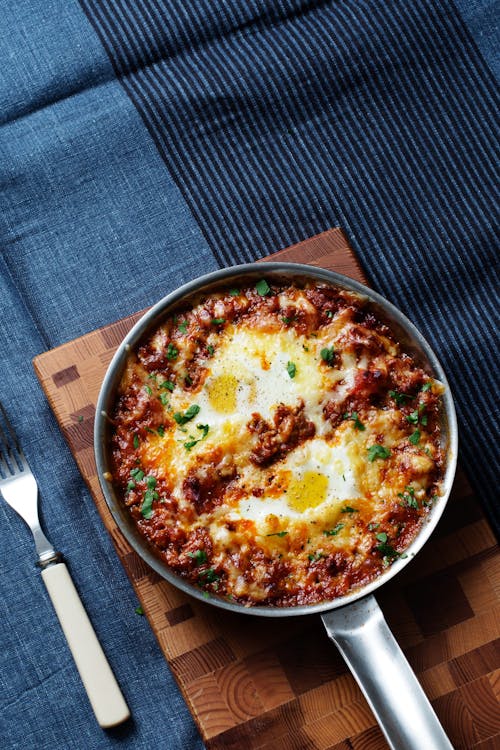
Here’s another great breakfast dish to make on a Sunday and warm up for fast breakfasts during the week. They freeze well, too. Protein (for three muffins): 39 grams; protein percentage: 30% - Keto baked eggs
Ground beef, turkey or pork — cooked with tomatoes, cheese, and topped with an egg — makes a hearty, filling breakfast dish. Protein: 41 grams; Protein percentage: 32% - Crispy bacon and kale with fried egg
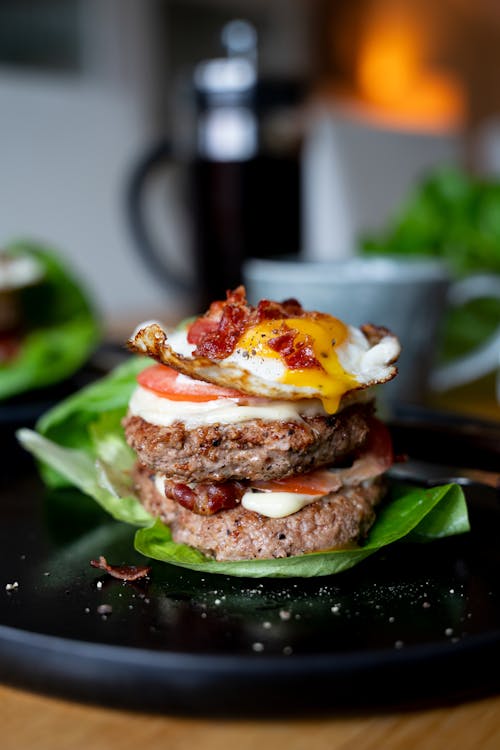
The sauteed kale, plus six slices of crispy bacon add 24 grams of protein to this dish. Fast and filling. Protein: 30 grams; Protein percentage: 32% - High protein turkey bacon breakfast burger
Call this dish the “hungry man breakfast!” A turkey or beef burger is combined with bacon, an egg, cheese, and tomato. Protein: 59 grams; Protein percentage: 37%.

Eggs disguised
We get it. Not everyone is crazy about eggs. And even if you happen to love ‘em, finding new ways to switch them up can add to the enjoyment and variety of your meals.So, try using eggs in delicious dishes that hide them. You’ll still get all their filling, nutritious protein without being so aware that you’re eating eggs.
Again, if you want to up the protein grams of your meal even more, add a side dish of plain Greek yogurt, ham, smoked salmon, cottage cheese, legumes, tofu, nut butter, or other sources of plant or animal protein.
Here are three high-protein recipes that include eggs, but in ways you’re less apt to notice:
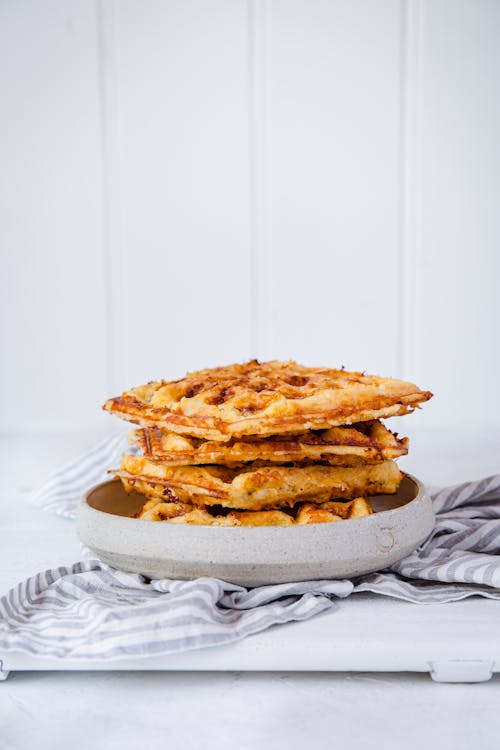
- Cheesy chaffles
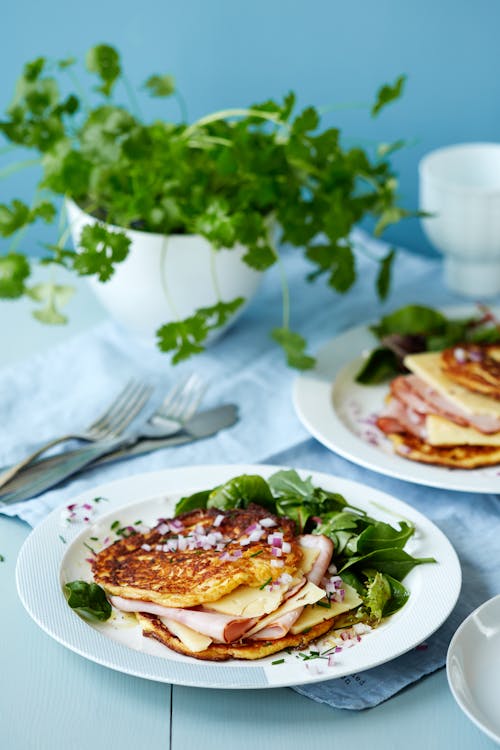
Low carb waffles are all the rage and no wonder: They are so tasty and make a great base for a wide variety of protein-rich toppings. Try them topped with 2 tablespoons of natural peanut butter (no sugar) or other nut butter, Greek yogurt, or cheese. Protein (for two waffles): 40 grams; Protein percentage: 24% - Croque Monsieur
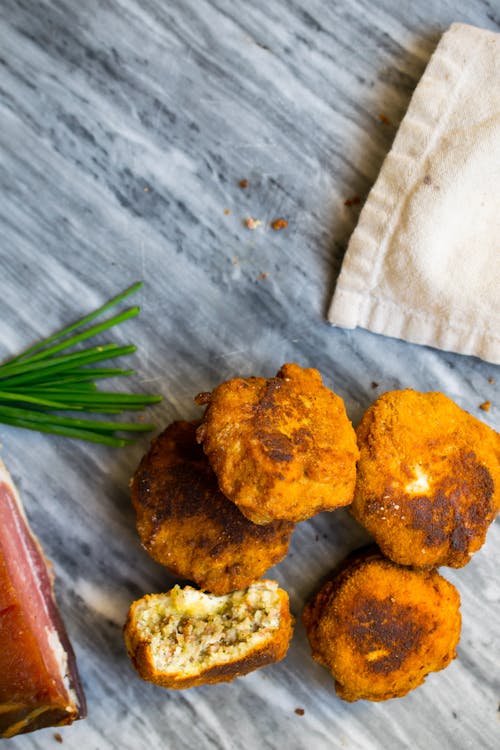
Two cottage cheese pancakes on the outside of a ham and cheese sandwich make this a filling, high protein meal. And if you add a fried egg on top, it makes it a Croque Madame. Protein: 42 grams; Protein percentage: 36% - Ham croquettes
Egg whites create the binding “glue” that keeps these tasty ham-based, fried croquettes together. Dip them in Greek yogurt seasoned with dijon mustard and herbs for extra protein. Three of them make a serving. Protein: 34 grams; Protein percentage: 28%
Egg-free




Eggs are not the only way to get lots of protein at breakfast. To keep your breakfasts varied and interesting, try some of our recipes where meat, cheese, or plant-based proteins take center stage.
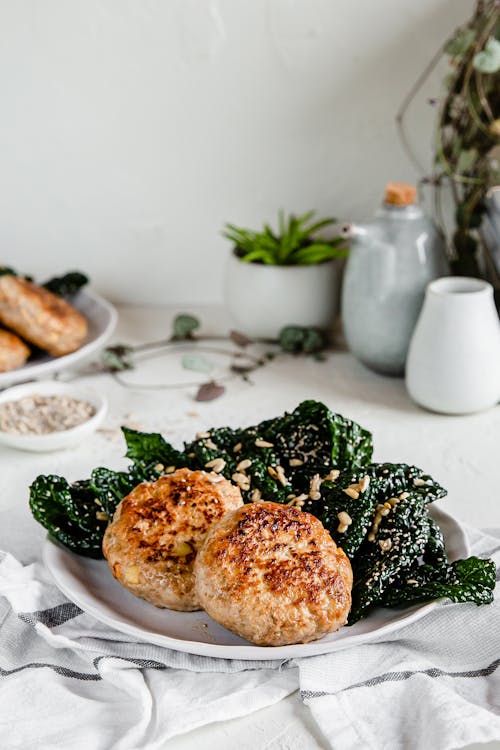
- Keto turkey apple patties with kale
Ground turkey combined with chopped apple and other seasoning makes a flavorful high protein pattie. Protein: 35 grams; Protein percentage: 31% - Cottage cheese breakfast bowl
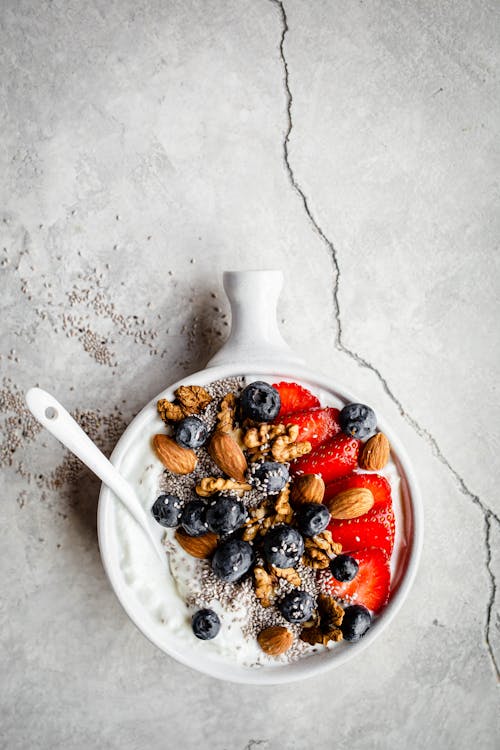
Cottage cheese and Greek yogurt, plus nuts, seeds, fresh strawberries, and blueberries make a fast and filling high protein breakfast. Protein 26 grams; Protein percentage: 26% - Keto breakfast tapas
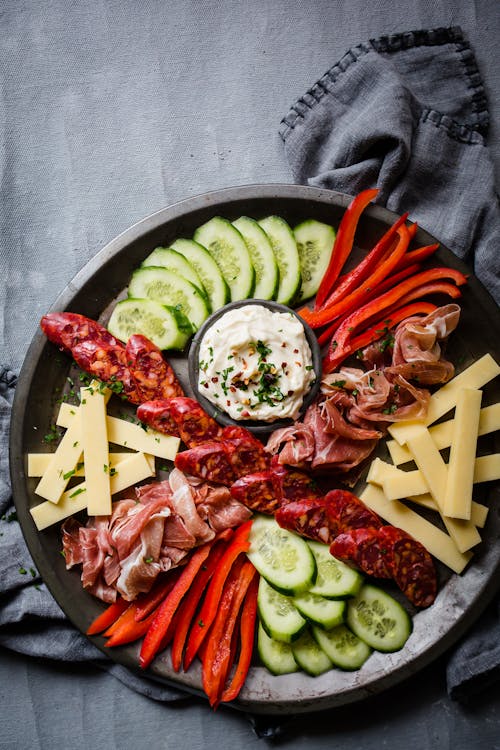
Who says that a charcuterie platter — with a variety of deli meats, cheese, and vegetables — is only for a party or pre-dinner appetizer? This quick, no-cook plate is perfect for breakfast, too. Swap in leaner meat, like sliced chicken breast or roast beef, or cottage cheese for a higher protein count and percentage. Protein: 24 grams; Protein percentage; 20% - Keto vegan tofu scramble
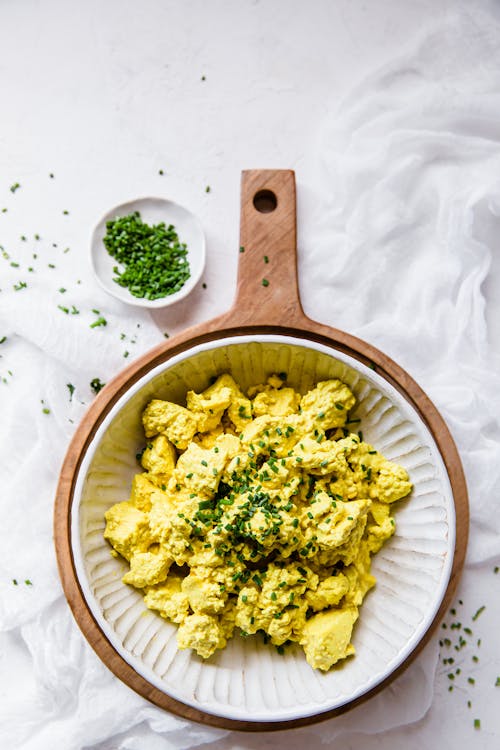
You don’t have to be vegan to appreciate this tasty way to serve protein-rich tofu. It’s seasoned with turmeric, nutritional yeast, and chives for a healthy kick. Protein: 35 grams; Protein percentage: 46% - Crispy marinated tofu
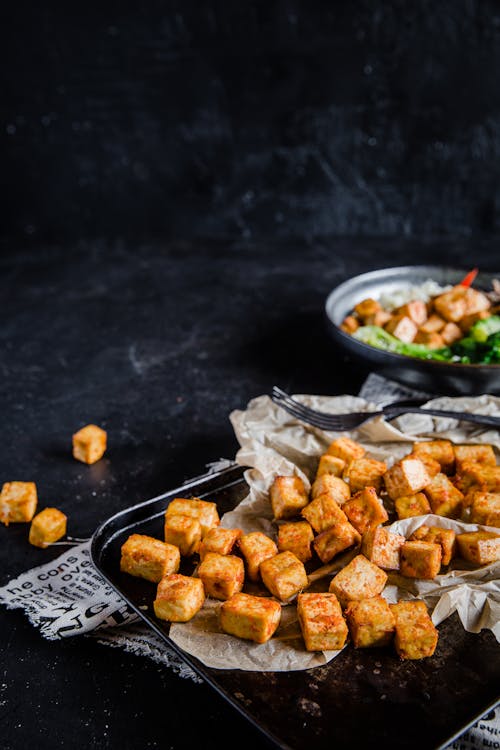
Tofu is a great plant-based protein source that can take on a wide variety of flavors. (Concerned about soy and health? See our soy policy.) Tofu is marinated overnight in a spicy mix of garlic, tamari and sesame oil, then baked until crispy. Protein 35 grams; protein percentage: 42%
No problem!

High protein smoothies
A protein-packed smoothie whipped up in a blender is always a great way to start your day. That’s because it’s quick, nutritious, and filling. Blend and go.Plus, you can make so many variations simply by blending in different ingredients. Using commercial protein powder, such as unflavored pea or whey powder, can boost the protein content of your smoothies. Diet Doctor recommends choosing protein powders with minimal extra ingredients.
- Low carb vegan protein shake
Coconut milk, almond milk, cinnamon, pea protein powder, and the secret ingredient of frozen cauliflower rice come together in this creamy, filling shake. Protein 28 grams; Protein percentage: 23% - High protein lime smoothie
Talk about simple and fast! Just blend cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, sour cream, with a bit of non-caloric sweetener and the refreshing addition of lime juice and zest. Protein: 20 grams; Protein percentage: 31% - High protein chocolate almond smoothie
Almond butter and almond milk, combined with cocoa powder and whey powder, are the key ingredients in this smoothie. But you can add other healthy items like avocado or berries. Protein: 28 grams; Protein percentage: 36% - High protein chocolate raspberry cheesecake smoothie
Cheesecake in a glass! Cream cheese, raspberries, cocoa powder and whey powder combine to make this decadent high protein drink. Protein: 25 grams; Protein percentage: 40%
Fish recipes








While some recipes call for fresh fish and seafood, remember that canned salmon, tuna, shrimp, crab, herring, and sardines are convenient, high protein options. You can always have them on hand in your pantry.
For example, frying a 5-ounce can of sardines and putting it on a bed of sauteed kale is a fast and easy breakfast that gives you 33 grams of protein and a protein percentage of 32%.
Here is a quartet of high protein fish options for breakfast.
- Low-carb salmon patties with feta cheese sauce
These savory, moist fish cakes are fast and filling. The tangy cheese sauce is the perfect complement for dipping. Protein: 43 grams; Protein percentage: 27% - Smoked salmon and avocado
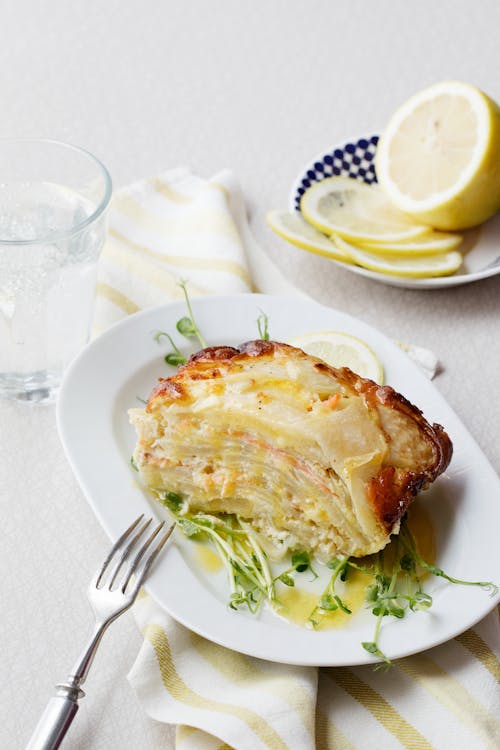
So simple: just smoked salmon and sliced avocado with a garnish of watercress and green onion. Protein: 31 grams; Protein percentage 32% - Smoked salmon kohlrabi gratin
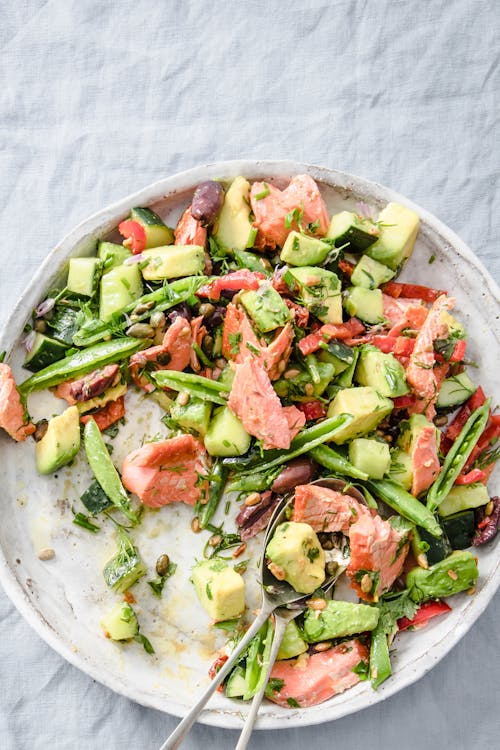
This make-ahead gratin that uses the radish-like vegetable kohlrabi rather than potatoes can be quickly reheated in the morning for even more intense flavors. Protein: 37 grams; Protein percentage 19% - Superfood salmon salad bowl
Salad for breakfast? Why not! Especially if it’s as simple, tasty, and nutritious as this Mediterranean-themed dish. Protein: 33 grams; Protein percentage 19%

Leftovers
You don’t need to go to a lot of trouble to make a protein-packed breakfast recipe. Just reheat high protein leftovers from the night before. Leftover steak, chicken, or pork, sliced on a bed of greens, or a warmed-up high protein casserole all taste just as good the next day.Diet Doctor is consistently adding more high protein meals to its collection. You can browse through some of our top high protein recipes here. Make enough for dinner to eat for breakfast or lunch the next day.
Why eat high protein?
Are you still wondering why you should start your day with a hefty serving of protein?Strong research evidence shows that eating more protein can help you lose weight, reduce your hunger, and keep your muscles strong without slowing your metabolism. 3
Eating high protein at your first meal sets you up to experience less hunger for the rest of the day. Studies of 116 diets in humans show that people on average may eat almost three times more calories on a low protein diet than on a very high protein diet. 4 Called protein leverage, this means when the body gets enough protein, its appetite for high-energy food is naturally reduced. So by consuming plenty of protein at the start of your day, in most cases, you will naturally consume less energy for the remainder of the day.5
Some research suggests that diets with increased protein can prevent or help treat type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, and possibly even reduce the risk of heart disease.6 In a recent trial, 100% of people with prediabetes who ate a high protein, moderate carb diet for six months achieved normal blood sugar levels.7
Higher protein intake also helps prevent a condition called sarcopenia, which is a loss of muscle mass that can occur as you age. Plus, it can help keep your bones strong, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, which is the loss of bone mass.8
Diet Doctor has lots of information and recipes to help you eat a high protein diet. Check out our other high protein guides:
Start your FREE 30-day trial!
Get instant access to healthy low-carb and keto meal plans, fast and easy recipes, weight loss advice from medical experts, and so much more. A healthier life starts now with your free trial!
Start FREE trial!25 high protein breakfast ideas - the evidence
This guide is written by Anne Mullens, Dr. Bret Scher, MD and was last updated on February 22, 2023. It was medically reviewed by Dr. Bret Scher, MD on July 21, 2022.
The guide contains scientific references. You can find these in the notes throughout the text, and click the links to read the peer-reviewed scientific papers. When appropriate we include a grading of the strength of the evidence, with a link to our policy on this. Our evidence-based guides are updated at least once per year to reflect and reference the latest science on the topic.
All our evidence-based health guides are written or reviewed by medical doctors who are experts on the topic. To stay unbiased we show no ads, sell no physical products, and take no money from the industry. We're fully funded by the people, via an optional membership. Most information at Diet Doctor is free forever.
Read more about our policies and work with evidence-based guides, nutritional controversies, our editorial team, and our medical review board.
Should you find any inaccuracy in this guide, please email andreas@dietdoctor.com.
Systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials — considered the strongest type of evidence — demonstrate that higher protein diets tend to help people feel full and retain muscle while losing weight:
Nutrition Reviews 2016: Effects of dietary protein intake on body composition changes after weight loss in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [systematic review of randomized trials; strong evidence]
Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2004: The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review [systematic review of randomized trials; strong evidence] ↩
Net carbs = total carbs minus dietary fiber. ↩
Systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials — considered the strongest type of evidence — demonstrate that higher protein diets tend to help people feel full and retain muscle while losing weight:
Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2004: The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review [systematic review of randomized trials; strong evidence]
Nutrition Reviews 2016: Effects of dietary protein intake on body composition changes after weight loss in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [systematic review of randomized trials; strong evidence] ↩
Annual Review of Nutrition 2016: Nutritional ecology and human health [overview article; ungraded]
↩Nutrition Research 2010: Consuming eggs for breakfast influences plasma glucose and ghrelin, while reducing energy intake during the next 24 hours in adult men [randomized controlled trial; moderate evidence]
Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2005: Short-term effect of eggs on satiety in overweight and obese subjects
[randomized controlled trial; moderate evidence] ↩American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008: Protein in optimal health: Heart disease and type 2 diabetes [overview article; ungraded] ↩
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2021: High protein diet leads to prediabetes remission and positive changes in incretins and cardiovascular risk factors [randomized trial; moderate evidence] ↩
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008: Role of dietary protein in the sarcopenia of aging [overview article; ungraded]
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008: Amount of type of protein influences bone health [overview article; ungraded]
↩