The biochemistry of insulin resistance




If you have an excess of glucose intracellularly, the liver will try to decompress itself by turning the excess glucose into fat. It exports this fat as VLDL, leading to high triglycerides and low HDL, and this fat may deposit itself in other visceral organs leading to fatty liver, fatty pancreas, and abdominal obesity. What’s the biochemical mechanism behind this? How does an overloaded cell block glucose entry into the cell? For this we need to discuss the citric acid cycle. (Warning: This discussion assumes some basic knowledge of biochemistry)
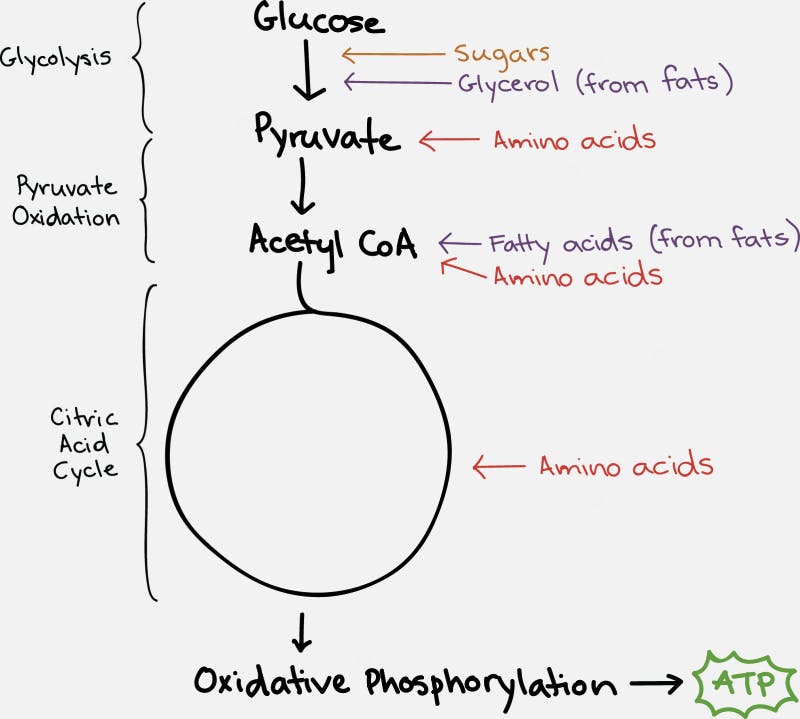



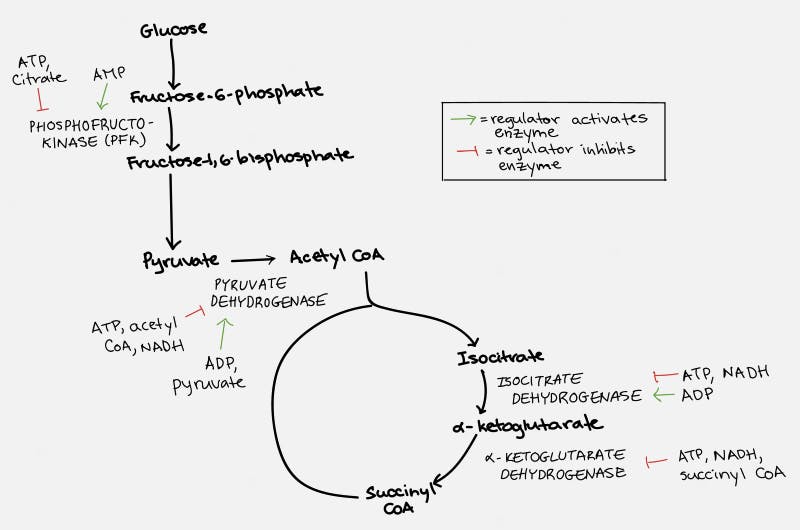
The TCA cycle, which takes place inside the organelle known as the mitochondrion, is pictured on the right. Glucose is first changed into pyruvate through the process of glycolysis (literally – the breaking down of glucose). Under anaerobic conditions, this can be used as a source of energy, with the end result being the production of lactic acid. But under normal aerobic conditions, it undergoes further pyruvate oxidation into Acetyl CoA. This can then undergo the TCA Cycle which generates the NADH and FADH2 necessary for the cell to undergo oxidative phosphorylation.
Each cycle of the TCA cycle regenerates the original substrate oxaloacetate so that it may continue running. Each Acetyl CoA provides 2 carbons, which get turned into carbon dioxide, but in the process generates 3 NADH and 1 FADH2, along with an ATP or GTP. So there’s not a whole lot of ATP generated with the TCA cycle directly. But indirectly, you can continue onto oxidative phosphorylation to generate 36 ATP per glucose, which requires the NADH and FADH2 for the electron transport chain.
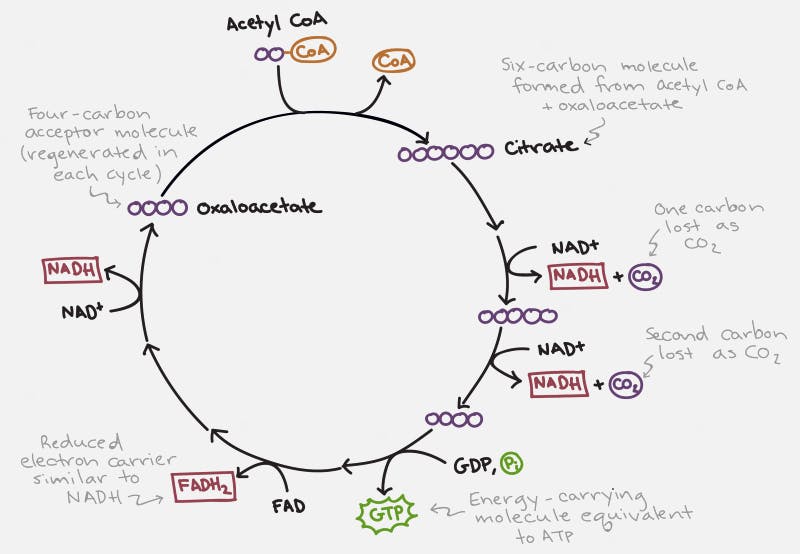



Fats (triglycerides) are broken into glycerol and their fatty acid chains. Glycerol enters similar to glucose. Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and combine with CoA to form acetyl CoA, which can enter the TCA cycle smoothly.
But what happens in the case that there is too much ATP? Consider an analogous situation. Suppose that you normally buy gasoline to power your car. You drive to and from work every day and you need about 50 liters or about 13 gallons. All of a sudden, instead of buying 50 L, you get 200 L per week. At first, you store some of the excess in your gas tank. When that gets full, you buy some jerry cans to store the extra. After that, it gets dangerous. All that excess gasoline is now sloshing around and pretty soon it’s going to explode like in a Tom Cruise Hollywood action movie.




The cell does this through a negative feedback loop. When there is too much ATP, the ATP itself — as well as some of the intermediates — acts upon the entire process to slow it down. When you are pumping gas into your gas tank and the tank gets full, the pump will automatically stop so that you don’t spill gasoline everywhere. The cell does the same thing.
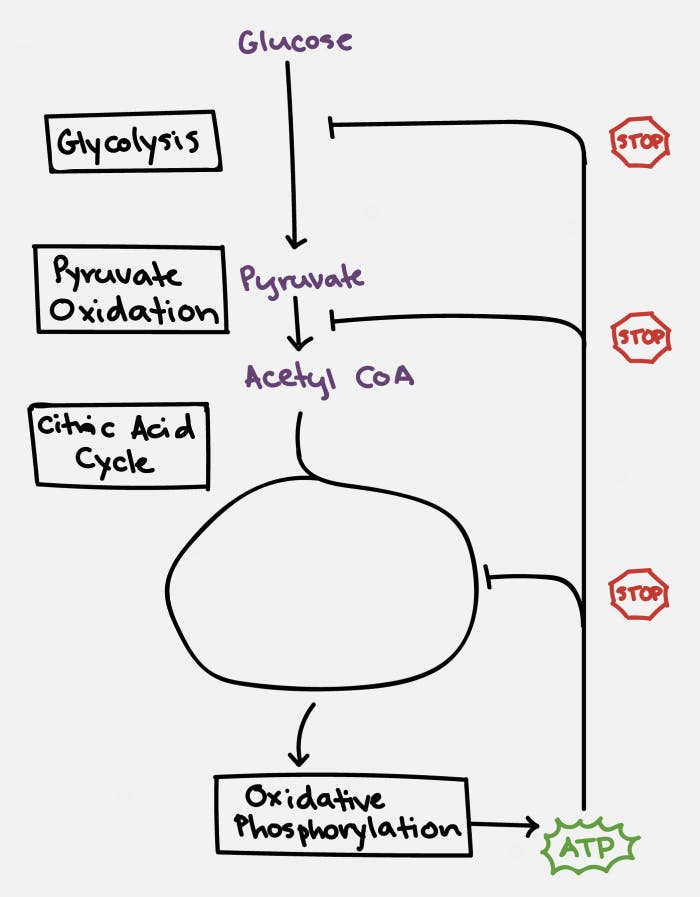



Specifically, ATP and citrate (remember this is one of the key molecules produced by the citric acid cycle) will inhibit the enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK), which blocks the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, the first step in the chain. ATP also blocks the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) to block the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA, the second step in the chain. ATP then acts at multiple sites within the TCA cycle to stop its own production.
This is a fantastically elegant system that ensures that ATP is produced when needed, but never to excess. When this process grinds to a halt, glucose, being at the very top of the chain, backs up. This slows down production of ATP and restores the system to normal. But what if we keep feeding glucose into the system?
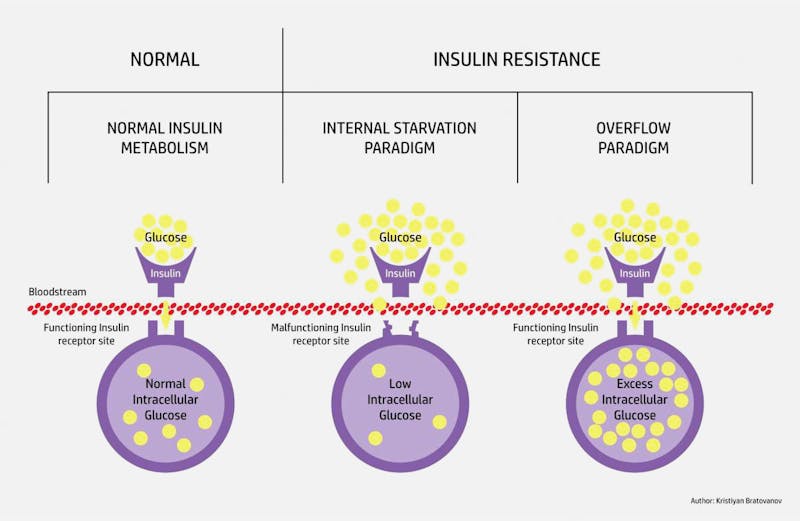
As glucose increases within the cells, there is less and less of a concentration gradient for glucose to flow from outside to inside the cell. Hence, you see the glucose increasing in the blood outside, and hence the term ‘insulin resistance’. But this is not a lock-and-key problem. It’s an overflow situation. The underlying problem of ‘insulin resistance,’ as the term is commonly used, comes down to two simple things – too much glucose, which leads to too much insulin.



- Don’t put more glucose into your body
- Burn off the glucose
You’ll also note that ‘insulin resistance’ while carbohydrate dominated, can also be activated through, for example, too much fat (triglycerides). Any macronutrient may produce ATP, which will overload the system and cause glucose to back up. The logical solution? Fasting. Boom.
Also published on idmprogram.com.
Dr. Fung’s top posts
Insulin
Type 2 diabetes
Weight loss
Keto
Intermittent fasting
More with Dr. Fung
Dr. Fung has his own blog at idmprogram.com. He is also active on Twitter.
Dr. Fung’s books The Obesity Code, The Complete Guide to Fasting and The Diabetes Code are available on Amazon.






































































































